How to Use Drum Granulator to Make NPK Fertilizer
Subtitle: Introduction to Drum Granulator
Drum granulation is a widely used method for producing NPK fertilizer, which stands for nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). NPK fertilizers are essential for promoting plant growth and enhancing crop yield. The drum granulator is a key piece of equipment in the NPK fertilizer production process. It is designed to transform raw materials into granules, making them easier to handle and apply to crops. In this guide, we will discuss how to effectively use a drum granulator to produce high-quality NPK fertilizer.

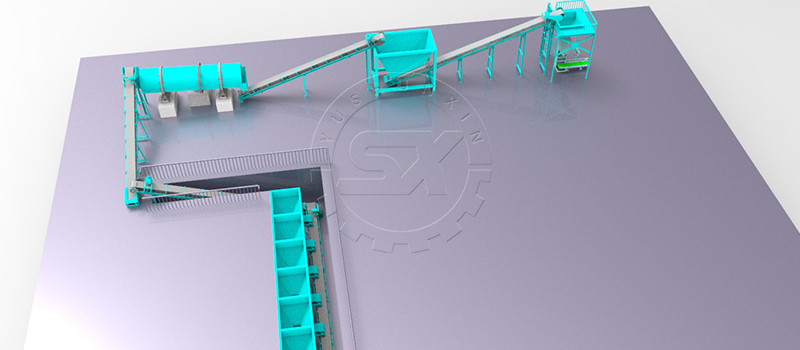
Powder to granules npk fertilizer making plant
Subtitle: Raw Material Preparation
Before operating the drum granulator, it is crucial to prepare the raw materials. The primary ingredients for NPK fertilizer are nitrogen-rich materials, such as urea or ammonium sulfate, phosphorus-rich materials like superphosphate or monoammonium phosphate, and potassium-rich materials like potassium chloride or potassium sulfate. Ensure that the raw materials are properly measured and mixed according to the desired nutrient composition.
Subtitle: Loading and Startup
- Position the Drum Granulator: Place the drum granulator in a suitable location with enough space for operation and maintenance. Ensure that the machine is stable and securely fixed.
- Connect Power Supply: Make sure the drum granulator is properly connected to a reliable power source. Double-check all electrical connections to avoid any safety hazards.
- Add Lubrication: Before starting the drum granulator, lubricate all the moving parts and bearings as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Proper lubrication will minimize friction and ensure smooth operation.
- Load the Raw Materials: Carefully pour the pre-mixed raw materials into the drum granulator’s feed hopper. Start with a small amount to test the equipment’s performance and adjust the feed rate accordingly.
- Start the Drum Granulator: Turn on the power supply and start the drum granulator. Pay close attention to any abnormal sounds or vibrations during the initial operation.
Subtitle: Granulation Process
- Adjust the Drum Angle: The drum granulator has an adjustable inclination angle. Set the angle based on the desired size and density of the fertilizer granules. A steeper angle will result in larger, denser granules, while a shallower angle will produce smaller, lighter granules.
- Control the Rotation Speed: The rotation speed of the drum granulator determines the residence time of the raw materials inside the drum. Adjust the speed to achieve the desired granulation effect. Higher speeds generally result in faster granulation, but excessive speed may lead to uneven granule formation.
- Spray the Binder Solution: Some NPK formulations require the addition of a binder solution to improve the granule strength and prevent crumbling. Use a spray system to evenly distribute the binder solution onto the raw materials as they tumble inside the drum granulator.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly monitor the granulation process to ensure optimal performance. Check the size, shape, and hardness of the granules. Adjust the operating parameters if necessary to maintain consistent granule quality.

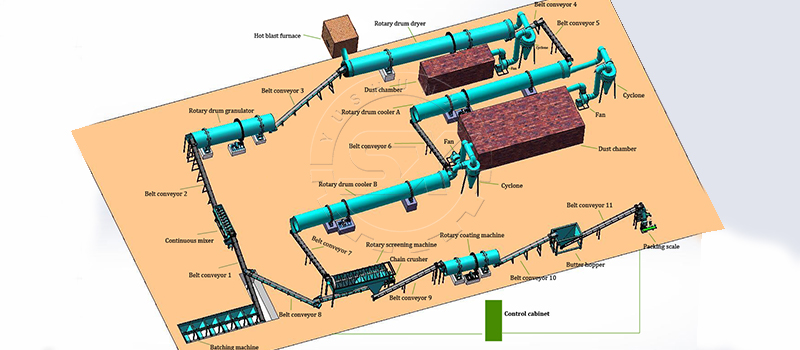
drum granulation machine
Subtitle: Drying and Cooling
After the granulation process, the newly formed fertilizer granules may contain excess moisture. Drying and cooling are essential steps to stabilize the granules and prevent caking during storage. Here’s how to accomplish this:
- Transfer to Dryer: Use a conveyor belt or similar mechanism to transfer the granules from the drum granulator to a drying system. The dryer should be equipped with appropriate airflow and temperature control settings.
- Drying: In the dryer, hot air is circulated around the granules to evaporate moisture. Maintain the correct temperature and drying time to achieve the desired moisture content in the final product.
- Cooling: After drying, the granules need to be cooled down to ambient temperature. This can be achieved using a cooling system, such as a rotary cooler or a fluidized bed cooler. Cooling helps prevent the granules from clumping together and facilitates subsequent packaging and storage.
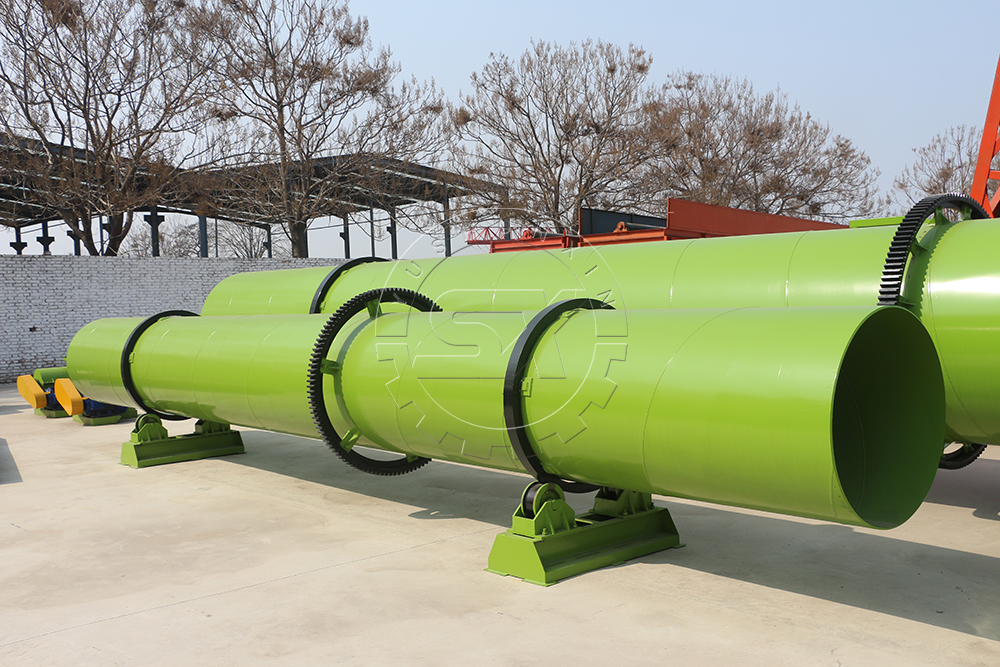

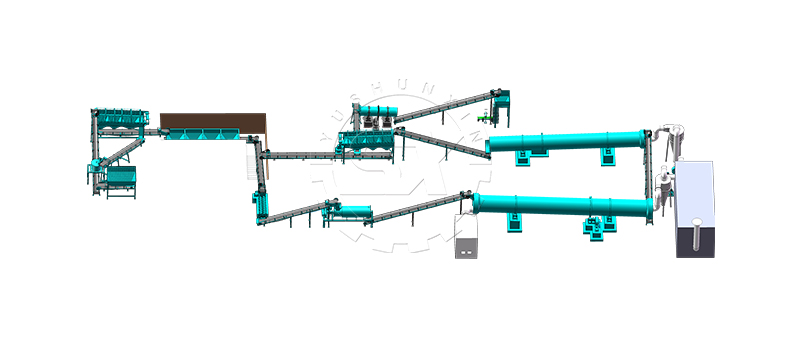
drying NPK fertilizer
Subtitle: Packaging and Storage
Once the NPK fertilizer granules have been dried and cooled, they are ready for packaging and storage. Follow these steps:
- Packaging: Use appropriate packaging materials, such as bags or bulk containers, to store the fertilizer granules. Ensure that the packaging is sealed properly to maintain product quality and prevent moisture absorption.
- Labeling: Clearly label each package with essential information, including the nutrient composition, batch number, manufacturing date, and any safety precautions.
- Storage: Store the packaged NPK fertilizer in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight. Follow recommended storage conditions to prevent degradation and maintain the granules’ quality and effectiveness over time.
Subtitle: Maintenance and Safety
To ensure the drum granulator operates smoothly and safely, perform regular maintenance and adhere to safety guidelines:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for routine maintenance tasks, such as lubrication, inspection of parts, and replacement of worn components. This will prolong the equipment’s lifespan and minimize downtime.
- Safety Precautions: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when operating the drum granulator. Follow safety protocols, such as isolating power supply during maintenance, and keep the work area clean and free from potential hazards.
By following these guidelines and understanding the granulation process, you can effectively use a drum granulator to produce high-quality NPK fertilizer. Remember to consult the equipment manufacturer’s instructions and seek expert advice when necessary to optimize your fertilizer production. For details you can visit https://www.fertilizerproductionproject.com/npk-fertilizer-production-line/.